The Function and Effects of THCa
Cannabinaceous plants are gradually revealing their secrets and advantages as more study is done. To the point that new phrases such as cannabidiol (CBD) and tetrahydrocannabinol (THC) have been coined to describe the therapeutic uses of cannabidiol (CBD) and psychotropic effects of tetrahydrocannabinol (THC), which were previously thought of a narcotic drug. Looking to try something new? Check out this.
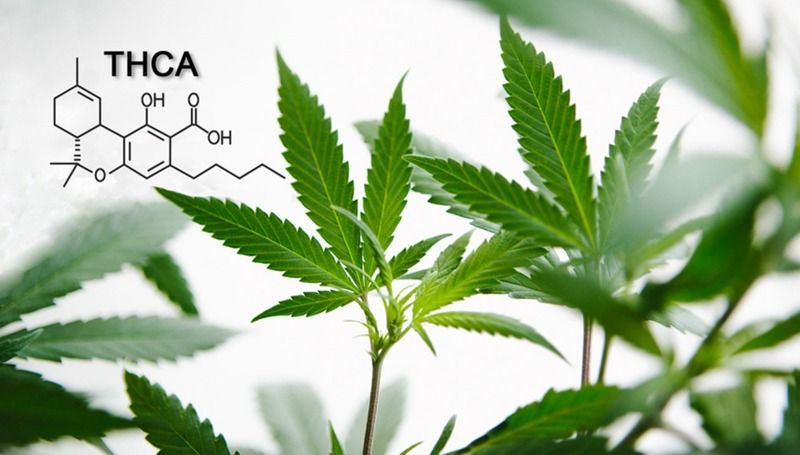
Do you know what THCa is? It’s a harsher chemical found in Cannabis Sativa plants, commonly known as Indian hemp. Its formal name is tetrahydrocannabinol, which means it’s an acidic molecule produced naturally by the Cannabis Sativa plant. THCa works with the central nervous system and endocannabinoid receptors in the same way as CBD and THC do. There are differences between them, despite their similar properties and impacts on the body and mind.
The Effects of Tetrahydrocannabinol on The Body
THCa’s research is still underway, but it has already illuminated some of the impacts of this cannabinoid component. Although no claims can be made regarding this cannabinoid component, here is a summary of its effects on the body:
- It appears to be an anti-emetic, in other words, it reduces vomiting, nausea and loss of appetite ;
- Like CBD, it seems to have an effect on neurodegenerative diseases such as Parkinson’s;
- THCa has an anti-inflammatory power useful for the treatment of many pathologies and diseases;
- Finally, it would be a practical anti-proliferant to inhibit the growth of cancer cells in the prostate.
How Does THCa Become THC?
9-Tetrahydrocannabinolic acid is not only an acid, but also the scientific moniker for what THCa becomes when it undergoes a process called decarboxylation.
Marijuana plants are completely safe to use. They have no negative side effects or impacts on the body. It’s a highly precise procedure that transforms the plant’s molecules into a psychoactive substance. In fact, there’s a reason why marijuana is dried, cured and burned before ingestion. THCa is converted to THC during decarboxylation.
The chemical reaction goes as follows: the carboxyl group of the herb is eliminated. This is caused by THCA’s thermal instability, which responds to changes in temperature and pressure.
To achieve this particular evolution, three criteria are needed:
- Long storage at room temperature;
- Exposure to direct sunlight for a long period;
- Smoking the cannabis bud.
THC vs THCa
The non-psychotropic cannabinoid present in raw and live cannabis is THCA or Tetrahydrocannabinolic acid, which has a chemical structure very similar to that of THC or delta-9-tetrahydrocannabinol. The psychotropic cannabinoid, THC, contains a Delta-9 nucleus. They have a near identical chemical makeup. THCa has an extra carboxyl group than does THC, hence the difference between the two cannabinoids
THCa does not bind well to CB1 or CB2 receptors in our endocannabinoid system. It is not psychotropic because of its three-dimensional form and larger size, which prevents it from fitting into CB1 receptors. It’s thought that THCa, as well as some other acid forms of cannabinoids, may act to inhibit COX-1 and COX-2 enzymes, resulting in the potential to reduce pain and inflammation. Prostaglandins are chemicals produced by both these enzymes that promote inflammation, discomfort, and fever.
How is THCa Converted Into THC?
THC is formed when THCa is decarboxylated, which entails a chemical change in which heat/light are used to remove one carboxyl group from cannabinoids. “Decarbing” allows various cannabinoids to bind more effectively with your endocannabinoid receptors.
Let’s review how we said that THCa had one more carboxyl group than THC? It loses the extra carboxylic acid group during decarboxylation and transforms to THC. The chemical structure change transforms it into the ideal form for CB1 receptors, laying the groundwork for THC’s euphoric mind-altering effects as we know them.
Decarboxylation occurs when raw cannabis is heated, either by:
- Sunlight
- Increased room temperatures
- Direct heat exposure via smoking, vaping, concentrates, and/or DIY carboxylation
Potential Benefits of THCa
We are decades away from completing the THCa research, and there is still a lot to learn. So far, it appears that THCa has the potential to be a therapeutic drug.
Here’s are some of the potential THCa benefits that have shown up in recent studies:
- Anti-inflammatory properties: As recently as this year, research has highlighted the anti-inflammatory properties of THCa. It’s also possible that THCa can help inhibit the enzymes that cause pain and inflammation.
- Protection against neurodegenerative diseases: THCa may serve as a safeguard against the damaging effects of neurodegenerative diseases.
- Anti-nausea: A study conducted in 2020 found THCa could be more effective than THC when it comes to reducing vomiting and nausea.
- Reduced obesity: THCa may reduce obesity and help decrease the likelihood of obesity-related diseases such as fatty liver disease and diabetes. The same study showed that the cannabinoid could help correct insulin resistance and glucose intolerance, critical factors in obesity-related diabetes.
How Does the Process Work?
When fresh flowers are dried and preserved, the process begins. When THCA is heated, a large number of the compound converts to THC. nHowever, when THCA is crystalline, it may be extracted and consumed in its purest form. Concentrates include THCA, and when crystalline, it can be extracted and eaten in its purest form. Because the purpose of cannabis extracts is to eliminate terpenes and flavonoids while isolating the cannabinoids, there’s little fragrance or taste.
Raw cannabis has a variety of health advantages for patients that use it in their treatments. Cannabis oils are full-spectrum because they are made from raw plants, and most users or patients can get their daily THCA intake by eating cannabis on a daily basis.
